
We get distracted by Urgent things that are not important-quadrant 3 activities-such as phone calls, text messages or interruptions from others. They're important, but once we finish dealing with the Urgent and Important crises, we often don't want to work in quadrant 2. These are the things we don't do because they're never urgent. Quadrant 2 activities include: all work in each of the 7 habits, maintenance, recreation, self-care, learning, reading, and relationship building. These are the things we cannot and should not ignore. Quadrant 1 activities are the things that are important and urgent: emergencies, deadline-driven projects, crises, some meetings, some phone calls. To be effective we need to take care of everything in quadrant 1 and then spend as much of our remaining time as possible in quadrant 2. There are four quadrants where we spend our time: We can use the time management matrix to determine where to spend our time. The idea is to have these clearly defined and on a piece of paper. It means defining your idea of success in life from the image you would like to leave in the roles that you assume (like spouse, grandparent, voter, activist, student, employee, manager). Basically it means doing life with your values in hand. Decide which of your roles and goals are most important, then determine what steps will best achieve those goals.

I want to be a good husband, to be a good father.
7 HABITS OF SUCCESSFUL PEOPLE DIAGRAM FULL
7 HABITS OF SUCCESSFUL PEOPLE DIAGRAM FREE
You have the opportunity to use your free will and hard work to change yourself and your circumstances. You will influence your life more than anyone else. This is the basis of all further habits and a cornerstone of success. Private victory, the path to independence Habit 1: Be proactive
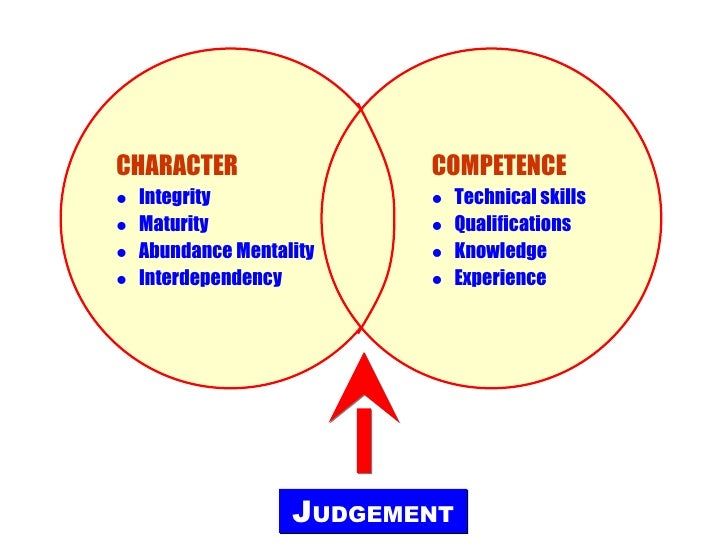
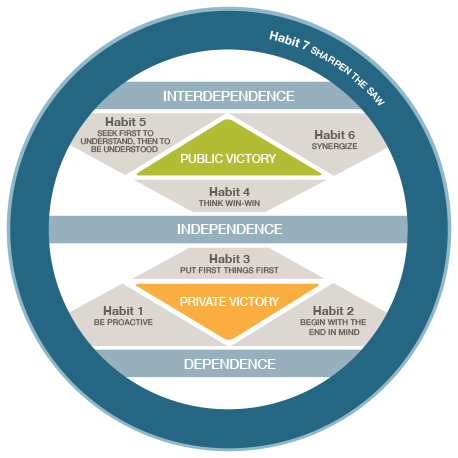
2.2 Habit 5: Seek first to understand, then to be understood.2 Public victory, the path to interdependence.1.2 Habit 2: Begin with the end in mind.1 Private victory, the path to independence.Regulating emotions and responding appropriately as well as responding to the emotions of others are all important aspects of emotional management. Managing emotions: The ability to manage emotions effectively is a crucial part of emotional intelligence and the highest level.For example, if your boss is acting angry, it might mean that they are dissatisfied with your work, or it could be because they got a speeding ticket on their way to work that morning or that they've been fighting with their partner. If someone is expressing angry emotions, the observer must interpret the cause of the person's anger and what it could mean. Understanding emotions: The emotions that we perceive can carry a wide variety of meanings.Emotions help prioritize what we pay attention and react to we respond emotionally to things that garner our attention. Reasoning with emotions: The next step involves using emotions to promote thinking and cognitive activity.In many cases, this might involve understanding nonverbal signals such as body language and facial expressions. Perceiving emotions: The first step in understanding emotions is to perceive them accurately.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
